Proxying Android Traffic
In this tutorial, we will cover the process of manually configuring an Android device to proxy its traffic through Caido.
WARNING
Caido is not liable for any malfunctions, failures, damages, loss/theft of data, or other technical issues that may occur with your device as a result of following this tutorial. Proceed at your own risk.
INFO
- This process does not require a rooted device.
- Be aware that the names and locations of settings options may vary between devices.
- Ensure to pay attention to any prompts on the device itself while proceeding through these steps.
- Ensure to restart your terminal after adding to the PATH environment variable.
TIP
If you want to automate this entire process, you can use apk-mitm.
Android SDK Platform-Tools: adb
To interface with the Android device using your computer's terminal, you will need the Android Debug Bridge (adb) which is included in the Platform-Tools package of the Android SDK.
Download the Platform-Tools for your operating system. Once downloaded, unzip the folder and make it globally accessible by adding it to your system's PATH environment variable.
To use abd with your Android device, navigate to the device settings and enable the Developer options. Then enable USB debugging.
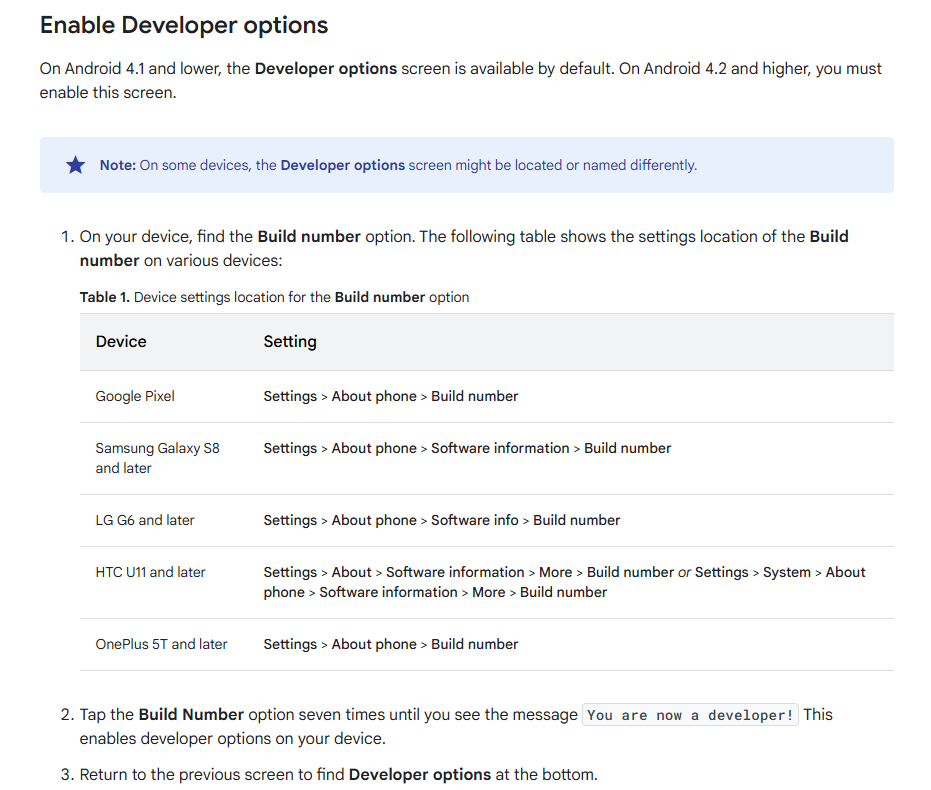
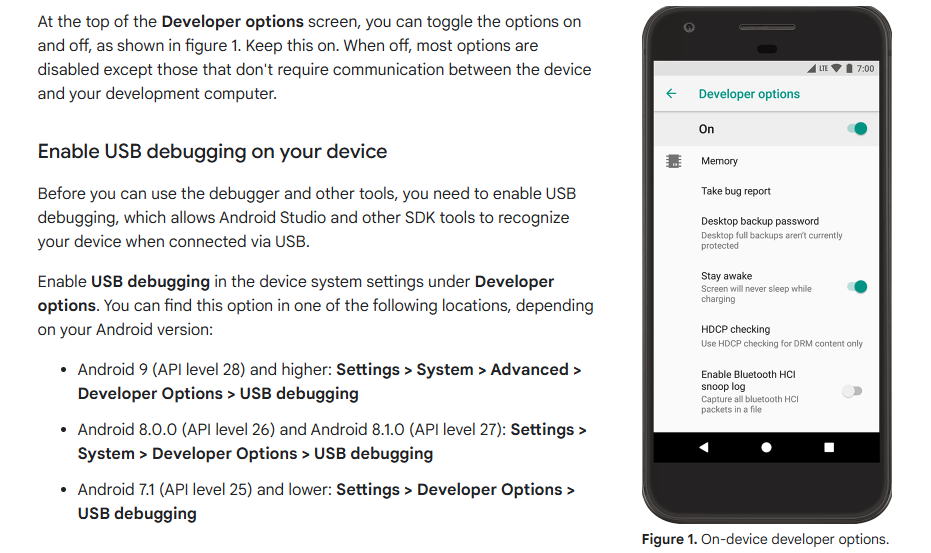
Connect the Android device to your computer over USB and verify the connection by running adb devices in your terminal. If the device is connected, it will be listed in the output.
TIP
If the command output lists the device as "unauthorized", disconnect and reconnect the device, and then accept the "Allow USB debugging?" permission prompt on your device.
Configuring the Android Device
To configure your Android device to use Caido:
- Ensure the device is on the same Wi-Fi network as the computer running Caido.
- Navigate to the device Wi-Fi settings and select your network SSID.
- Access the
Advancedsettings of the network and select theManualoption from theProxydropdown menu: - Set the proxy address to:
127.0.0.1:8080
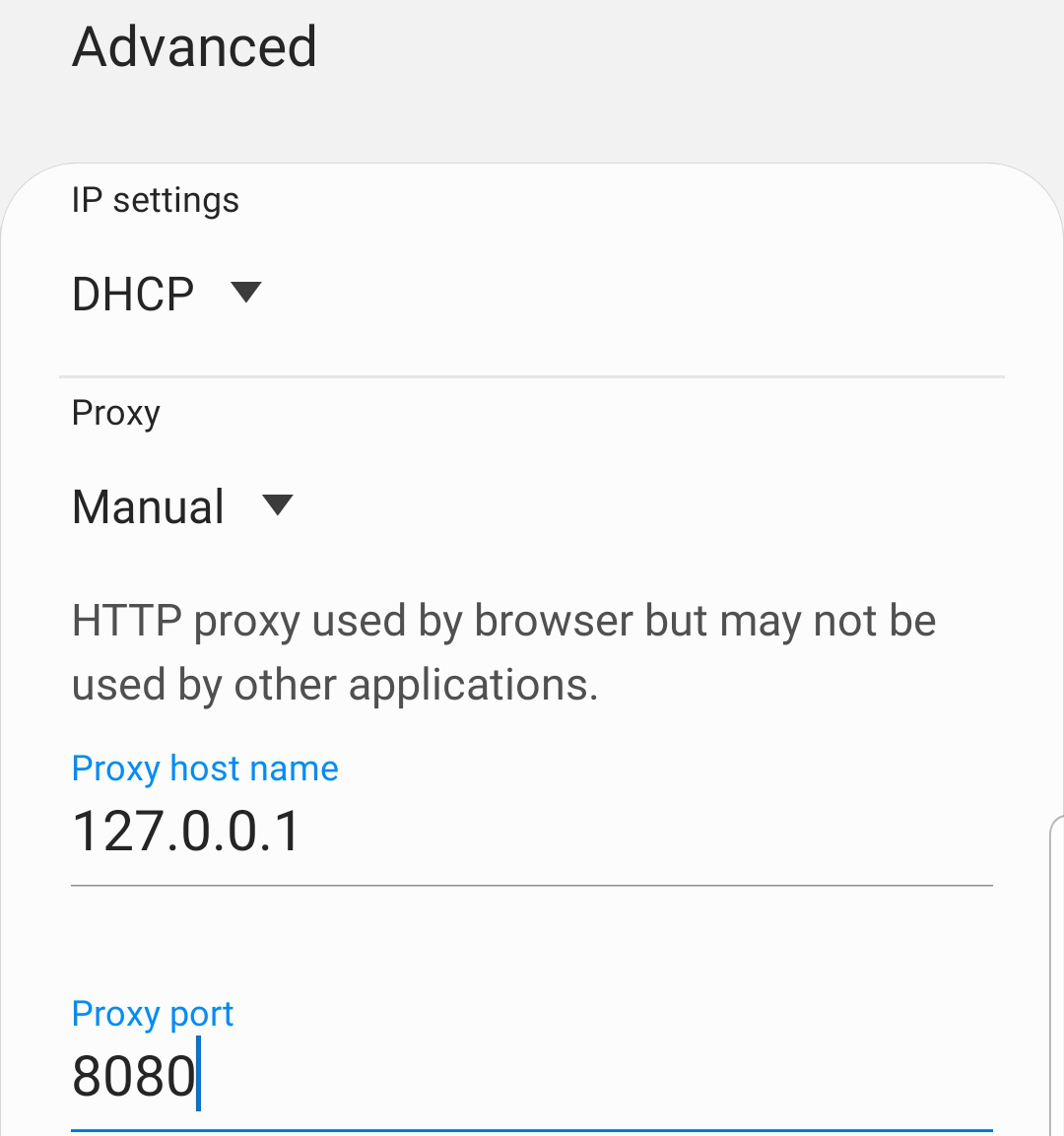
- Click
Saveto set the proxy configurations.
Port Forwarding
Since Caido is running on your computer, not your phone - run the following command to forward traffic from localhost:8080 on your device to port 8080 on your computer through the USB connection:
adb reverse tcp:8080 tcp:8080TIPS
If the command output contains the message "adb.exe: device unauthorized", accept the permissions prompt on your device, run
adb kill-serverand thenadb reverse tcp:8080 tcp:8080again.To verify the proxy is working, run
adb shell settings list global.To check if the app is actually using the proxy, run
adb shell dumpsys connectivity | grep -A 2 "Active network".
Intercepting Mobile Browser Traffic
- Navigate to http://127.0.0.1:8080/ca.crt in your device's browser to download Caido's CA certificate. Provide an arbitrary certificate name and select
Wi-Fiin theUsed fordropdown menu.
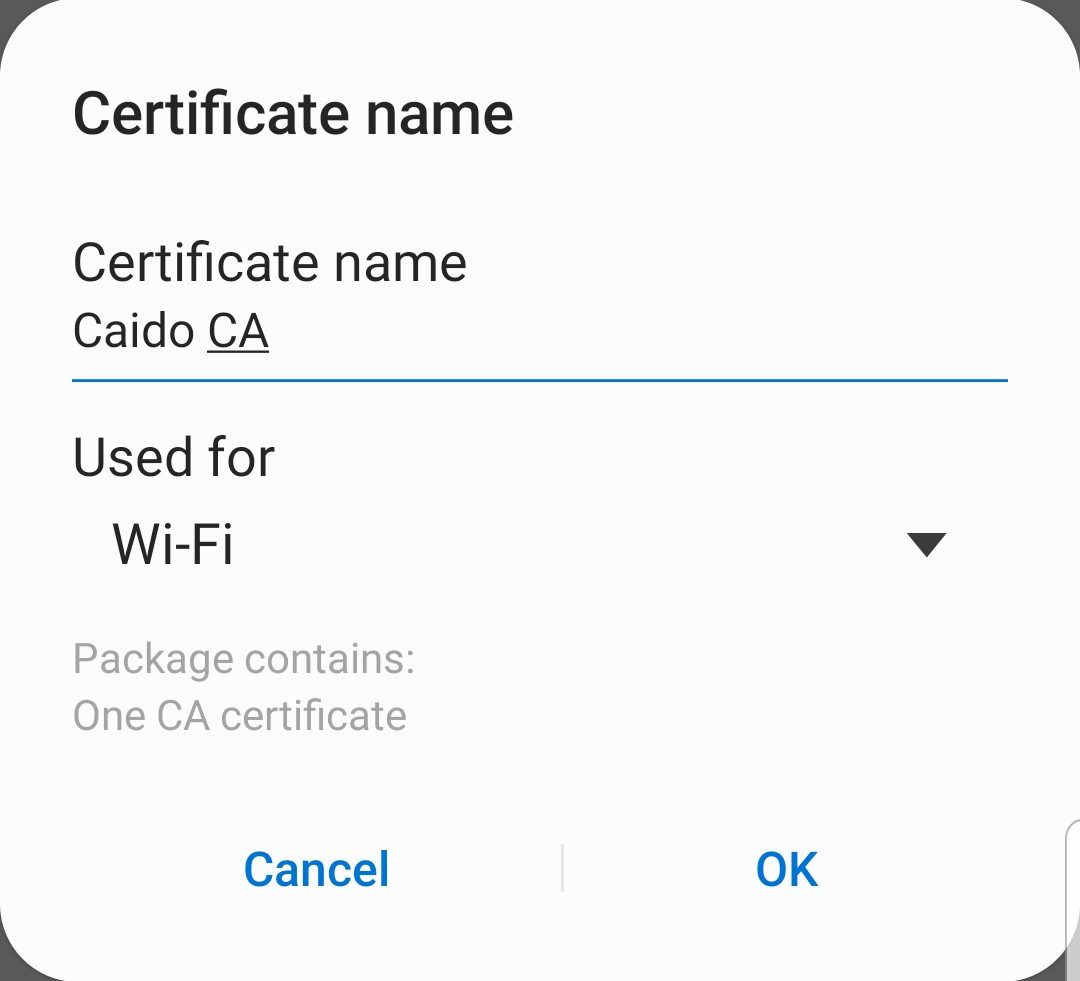
- Click
OKand navigate to a website using your device's browser, you will now see the traffic in Caido's HTTP History.
Intercepting Application Traffic
Android mobile applications are files bundled as .apk (Android Package Kit) packages and must be modified for use with Caido.
NOTE
In this tutorial, we’ll use the HTTPToolkit Pinning Demo application to demonstrate how to modify an APK so that Caido can proxy its traffic, and we’ll test these changes using the app’s various HTTP requests. If you are new to mobile application testing, we recommend you download the HTTPToolkit SSL Pinning Demo APK to ensure the steps align exactly.
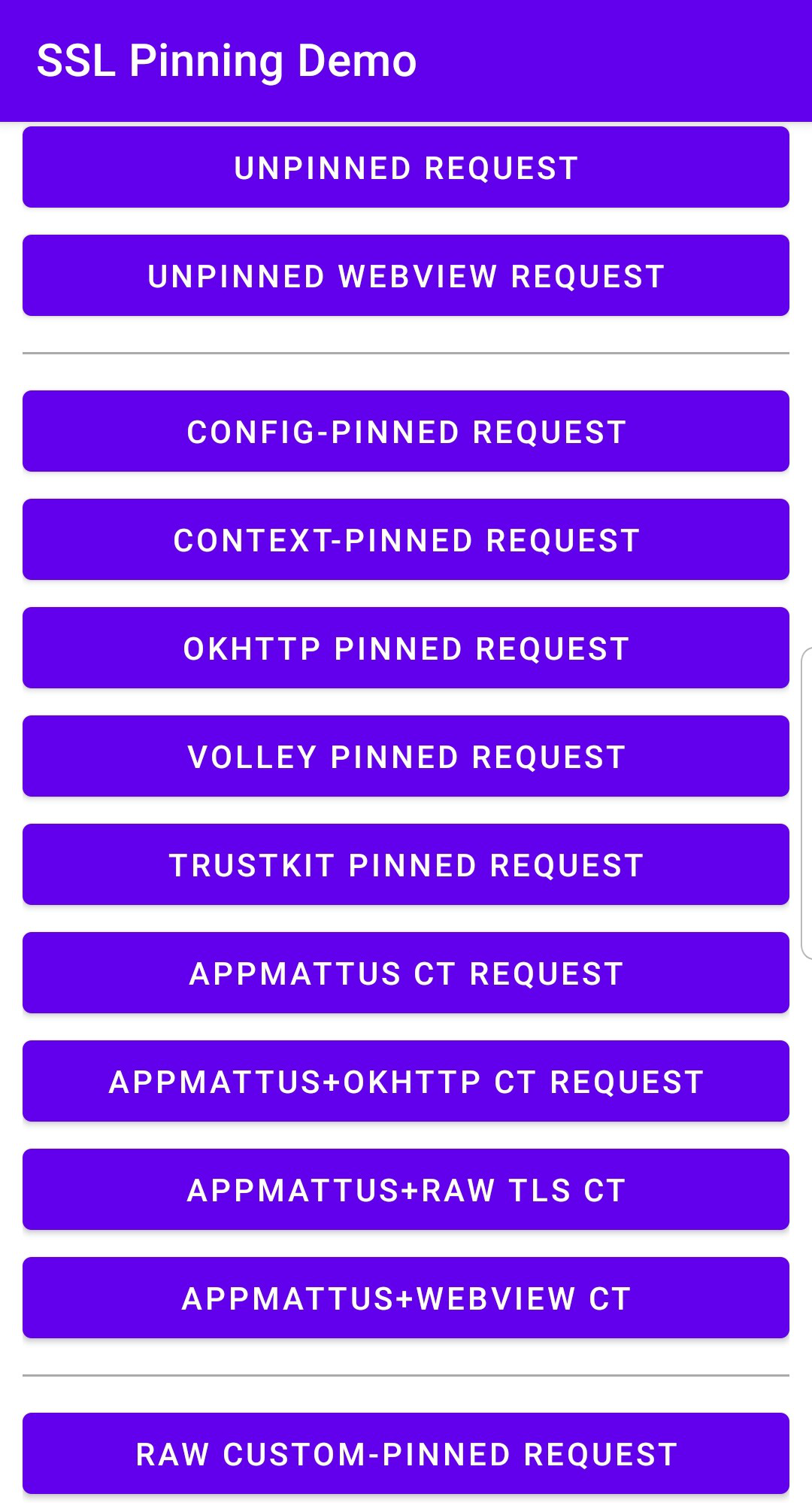
Once downloaded, install the application to your connected device with:
adb install pinning-demo.apkAPKs can be acquired by downloading them directly from repositories or sites such as apkmirror.com or apkpure.com.
APKs can also be extracted from applications already installed on your device. Expand this section to learn how.
- Initialize a command-line interface on your Android device:
adb shell- Find the application's
base.apkpackage on your device by listing all the file paths of installed packages and filtering the results by the application name:
pm list packages -f | grep -i pinning
Copy the location and exit the device command-line interface using
CTRL+Dor by typing and enteringexit.Pull the
base.apkfrom your device to your computer (do not include the=<package-name>portion of the output):
adb pull /data/app/tech.httptoolkit.pinning_demo-1wMoq8214ewjz2S-xt-sCA==/base.apkUnpacking APKs
Apktool is a tool for reverse engineering Android applications. Once you have an application's APK, with Apktool you can decompile the package into its individual resources (such as XML files, images, and code) and then rebuild them after making modifications.
Download Apktools for your operating system.
To unpack the contents of an APK to a new directory within the current directory, use the following command:
apktool d -o unpacked pinning-demo.apkIf you extracted the APK, ensure to replace pinning-demo.apk with base.apk.
Modifying the Network Security Configuration File
One of the reasons that Caido may not be able to proxy the application traffic is due to the presence of a Network Security Configuration file. Introduced in Android 7.0 (API level 24), the network_security_config.xml file allows developers to customize network security settings for their applications.
Open the
/res/xml/network_security_config.xmlfile, or if it doesn't exist, create it.Replace or write the content of the file to:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<network-security-config>
<!-- Base configuration that applies to all connections if not overridden. -->
<base-config>
<!-- Define which certificates should be trusted as root CAs (trust anchors). -->
<trust-anchors>
<!-- Trust the pre-installed system certificates. -->
<certificates src="system" />
<!-- Trust user-installed certificates (like Caido's CA) and allow them to override certificate pinning. -->
<certificates src="user" overridePins="true" />
</trust-anchors>
</base-config>
</network-security-config>Ensure that the main configuration file,
AndroidManifest.xmlreferences thenetwork_security_config.xmlfile via theandroid:networkSecurityConfig="@xml/network_security_config"attribute in the<application>tag. If you created a newnetwork_security_config.xmlfile, you will have to explicitly add this.From the directory of the unpacked APK, repack it with:
apktool b -o modified.apk ./
- You will need the
keytoolandjarsignertools in order to repack the APK. These tools are included in the Java Development Kit (JDK).
Download the JDK for your operating system and add it to your system's PATH environment variable.
- Generate a signing key with:
keytool -genkey -v -keystore custom.keystore -alias aliasname -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -validity 10000
- Sign the APK with:
jarsigner -keystore custom.keystore -verbose modified.apk aliasname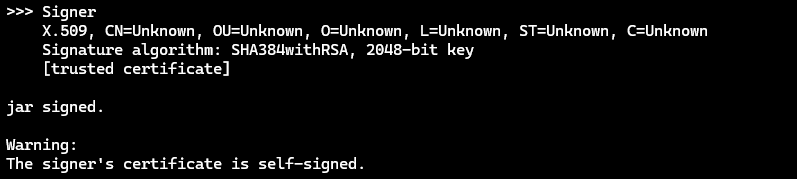
- Uninstall the original application from the device:
adb uninstall tech.httptoolkit.pinning_demo- Install the modified APK:
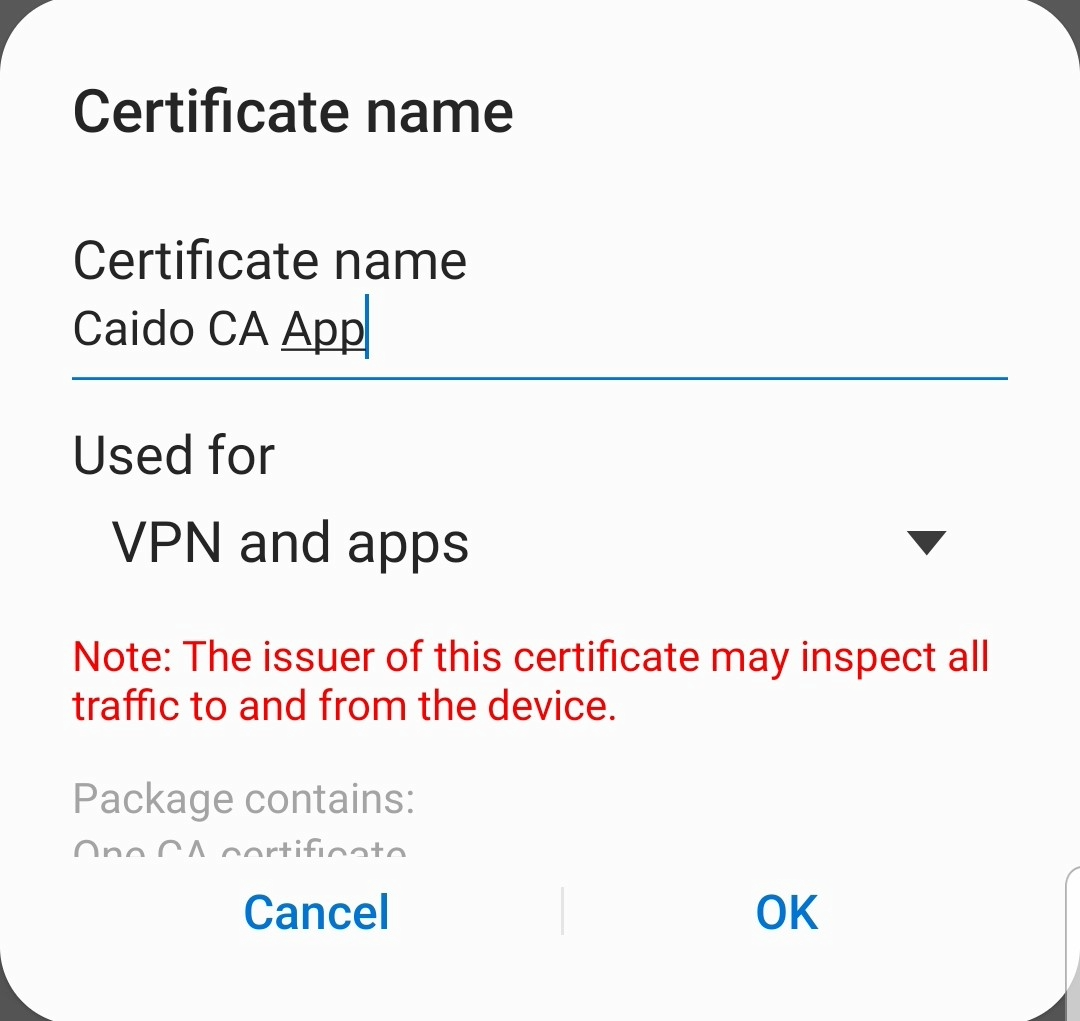
adb install modified.apk- Navigate to your device settings and search for "certificates". Select
Install from phone storageand select Caido's CA Certificate. ClickDoneto continue. Provide an arbitrary certificate name. This time select theVPN and appsoption in theUsed fordropdown menu. ClickOKto save.
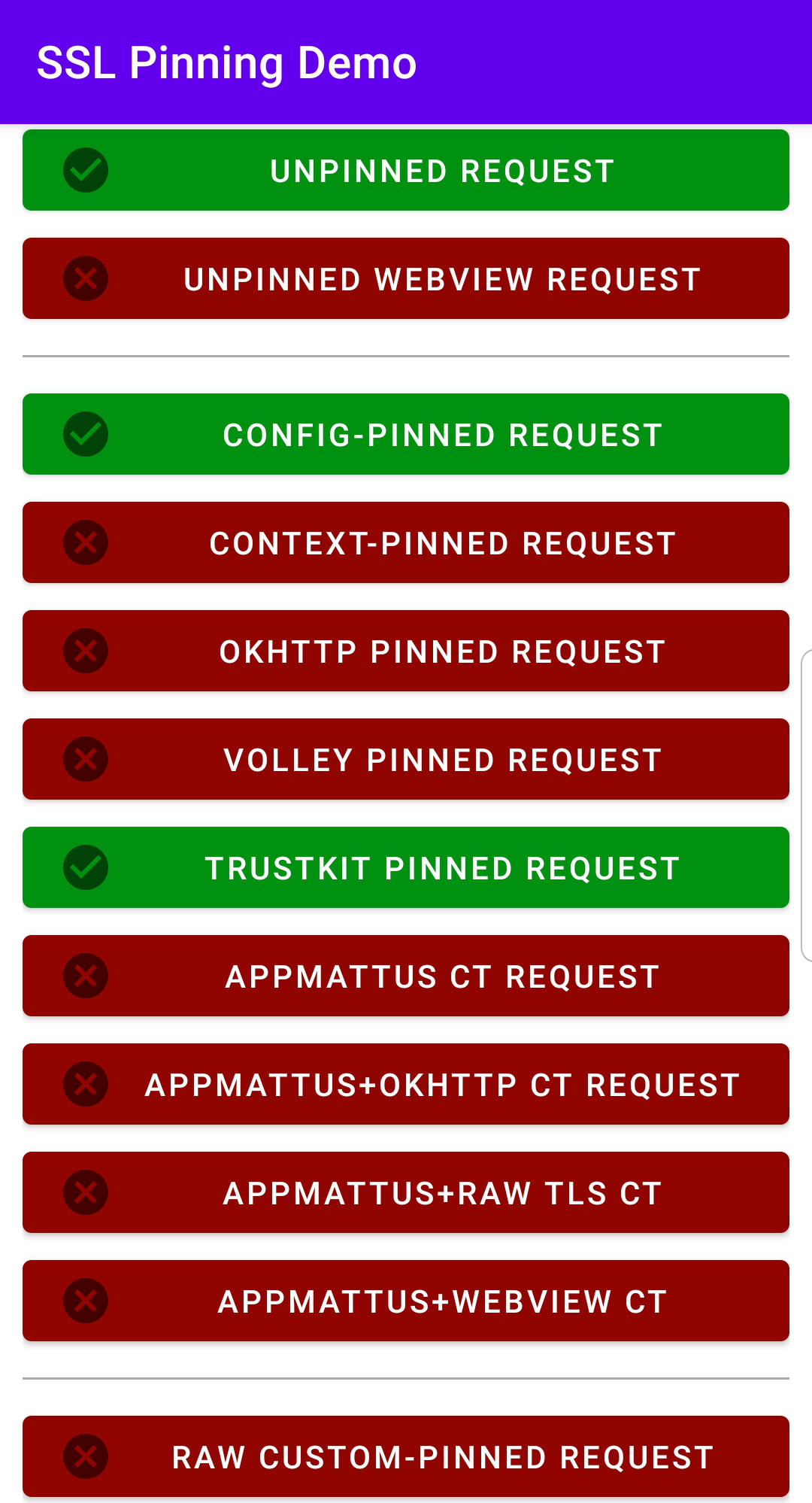
- Next, open the HTTPToolkit application on your device. You should be able to make the following requests:
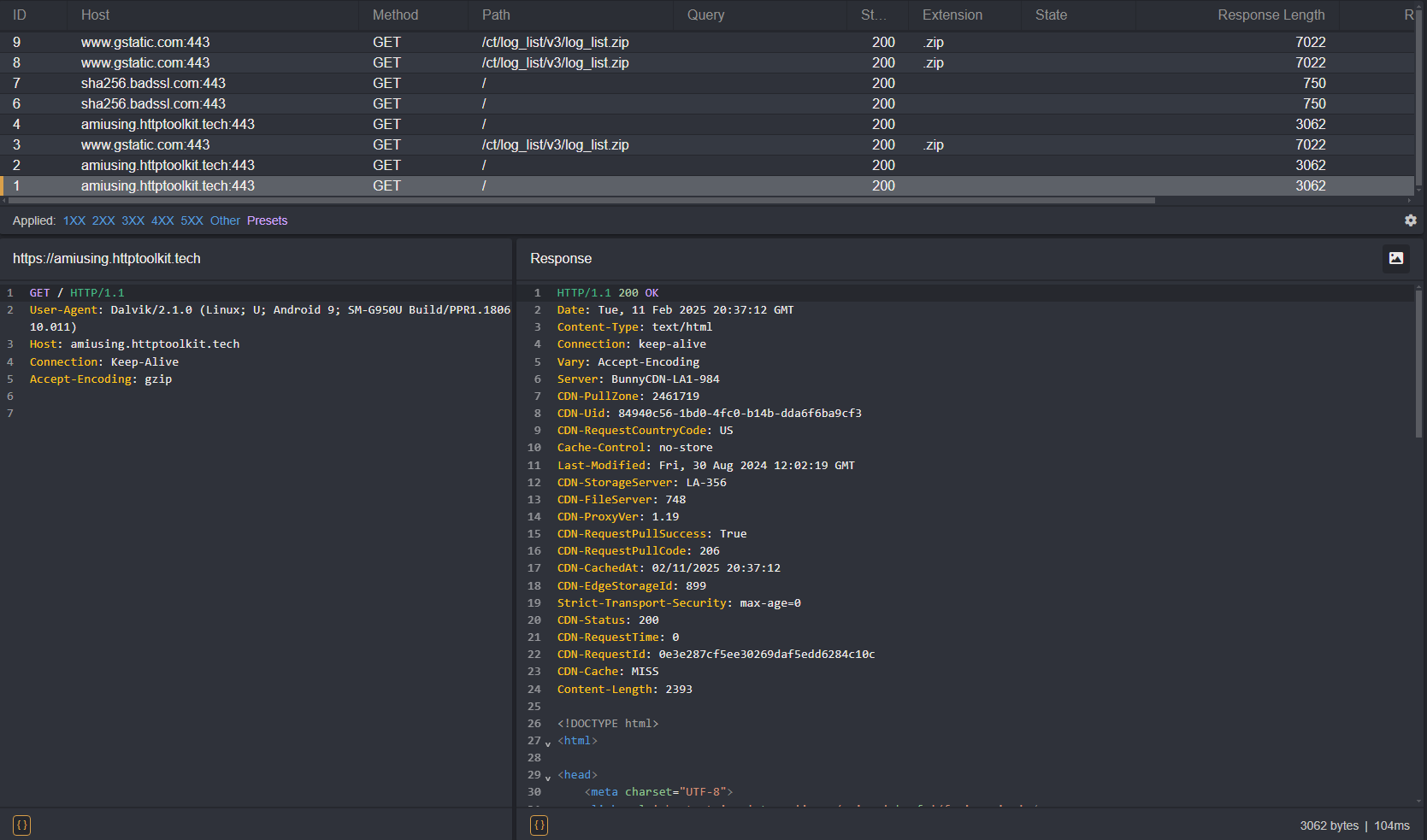
- You will now see traffic generated by the application in Caido's HTTP History.
Known Issues
As you can see, certain requests result in an error message and are not proxied through Caido. This is due to additional security measures.
If you are unable to navigate the application and are still not seeing its traffic in Caido, continue to the Intercepting Certificate Pinned Application Traffic tutorial.
